Product Version: 6.5.X.X
Overview
This article provides an overview of the various categories of Windows patches, their classifications, and the methodologies employed in deploying these patches using Saner CVEM. Understanding the types of updates and the patch deployment process helps organizations maintain a secure and up-to-date Windows environment.
Types of Windows KB Updates
Critical Update
Addresses critical non-security issues within the Windows operating system.
Released worldwide to ensure OS stability and reliability.
Definition Update
Enhances or modifies the definition database embedded within the OS.
Ensures up-to-date detection for threats, malware, and system definitions.
Driver Updates
Target one or more device drivers to improve hardware compatibility and functionality.
Security Updates
Address vulnerabilities identified in the OS by Microsoft or external security organizations.
Globally released and notified to users to mitigate potential security risks.
Feature Pack Updates
Modify specific OS features and functionalities.
Initially released to select users; positive feedback may lead to integration in the next major Windows release.
Windows 10 typically receives two feature updates annually.
Monthly Rollup
Released every second Tuesday of the month.
Consolidates all updates from the previous month and includes new malware definitions.
Patch Deployment via Saner CVEM
Saner CVEM simplifies patch management by integrating with the Windows Update API and WSUS (Windows Server Update Services). The deployment process is as follows: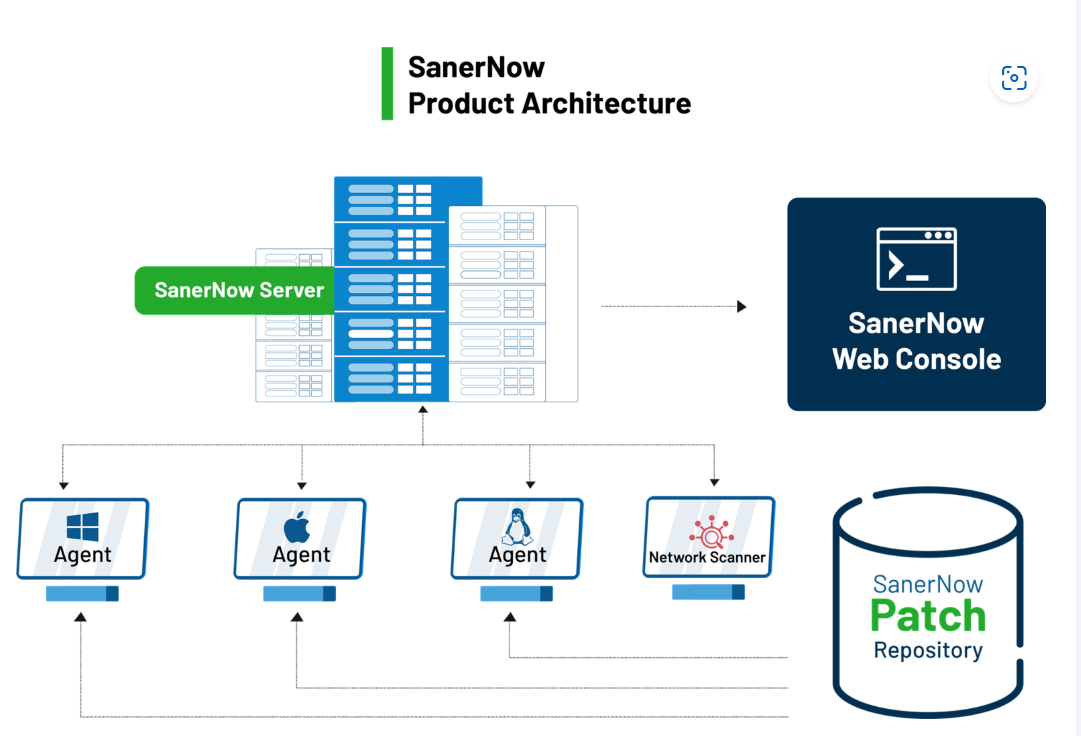
Selection of Patches
Administrators select missing patches from the “Missing Patches” section in Saner CVEM.
Integration with Windows Update API
The Saner CVEM API communicates with the Windows Update API.
It connects to the configured repository on the device (WSUS or Windows Update) to download required patches.
Windows Update Process
Update Discovery
The Windows Update Orchestrator periodically checks the Microsoft Update server or WSUS endpoint.
Randomized intervals are used to prevent server overload.
Searches for updates added since the last discovery, ensuring only new or missing updates are identified.
Download Process
Relevant updates are automatically downloaded in the background by the Windows Update Orchestrator.
Background downloading ensures minimal disruption to device usage.
Metadata and Arbiter Execution
When an update is applicable, associated metadata and the Arbiter are downloaded.
The Arbiter collects device information, compares it with the metadata, and generates an “action list” based on Windows Update settings.
Update Installation and Restart
If automatic installation is enabled, the Windows Update Orchestrator installs the update.
Devices may automatically restart post-installation to ensure full update implementation and maintain system security.
References
Microsoft Windows Update Documentation: https://support.microsoft.com
Saner CVEM Product Guide
Was this article helpful?
That’s Great!
Thank you for your feedback
Sorry! We couldn't be helpful
Thank you for your feedback
Feedback sent
We appreciate your effort and will try to fix the article